Marginal Cost Marginal Revenue Graph
Marginal cost Markup pricing: combining marginal revenue and marginal cost Monopoly market power monopolies marginal revenue demand cost price monopolist outcome firm quantity perfect competition sloping downward economics equals why
Marginal Cost | Definition | Calculation | Graph and Example
Monopoly monopolistic competition profit market long cost short structure run equilibrium monopolists efficient revenue maximizing price marginal making average quantity A monopolist faces a demand curve p = 70 Marginal revenue cost equals profit when gif
Marginal cost graph below depicts revenue average total curves mc atc mr firm price competitive perfectly will purely
The study economics for ma ignou microeconomics macroeconomicsMarginal revenue mc 2q cost monopolist profit socratic deadweight associated compute maximizing Marginal revenue labour market curve mrp returns diminishing ppt powerpoint presentationMonopolistic competition market structure.
Marginal cost and marginal revenueMarginal revenue cost Revenue marginal graph consider demand cost average solved total mr problem been hasSolved consider the graph of demand (d), marginal revenue.

Marginal revenue cost monopoly profit output maximizing price quantity monopolist costs curve total average economics benefits graph firm maximum profits
Market power and monopolyMarginal cost between mc graph curve avc example relationship Revenue cost marginal total quantity costs economics pure econ competition solve market will microeconomicsPricing marginal cost markup revenue profit point combining economics prices exceeds marked maximizing quantity left figure optimal theory applications.
Reading: choosing output and priceMaximizing profit when marginal revenue equals marginal cost Economics archive.
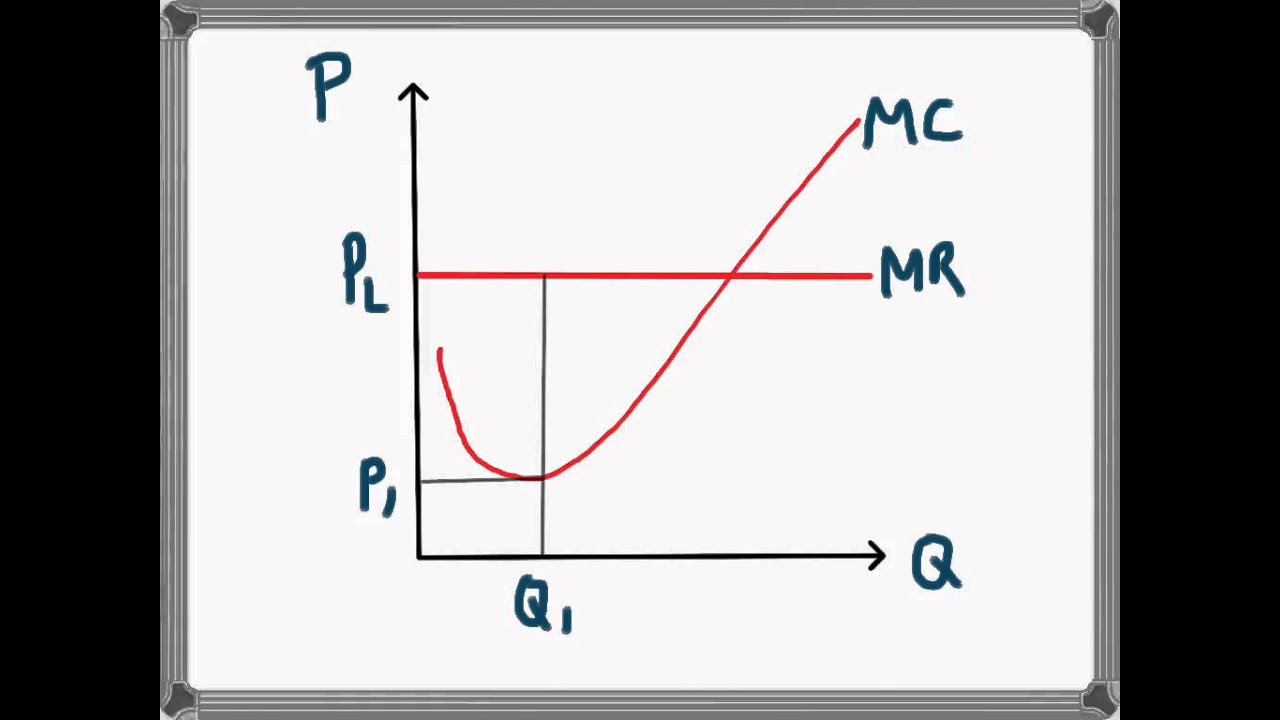

Monopolistic Competition Market Structure | Intelligent Economist

Reading: Choosing Output and Price | Microeconomics

PPT - Labour Market PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:4367631

Markup Pricing: Combining Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost

A monopolist faces a demand curve P = 70 - 1Q, with marginal revenue MR

The Study Economics for ma ignou Microeconomics macroeconomics

Market Power and Monopoly

Economics Archive | November 14, 2016 | Chegg.com

Maximizing Profit When Marginal Revenue Equals Marginal Cost

Marginal Cost | Definition | Calculation | Graph and Example
